BIO 385 — Invertebrate Zoology | |||
Invertebrate Diversity
| |||
Subphylum Crustacea
| ||||
Class Branchiopoda | |||
Order Anostraca
|

Brine Shrimp (aka Sea Monkeys), Artemia franciscana |
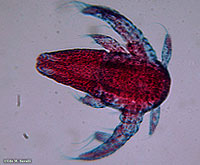
Brine Shrimp, Artemia sp., Nauplius larva |

Red-tailed Fairy Shrimp, Streptocephalus sp., female |
Order Notostraca
|

Longtailed Tadpole Shrimp, Triops longicaudatus |

Longtailed Tadpole Shrimp, Triops longicaudatus, ventral view | |
Order Cladocera
|

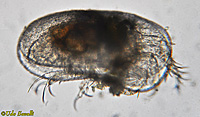
Water Flea, Daphnia magna See also labeled photo. |

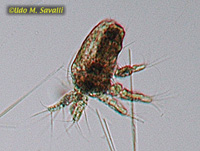
Water Flea, Moina sp., ventral view |
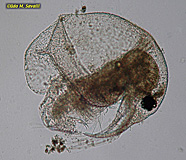
Water Flea, Bosmina sp. |
"Conchostraca"
|
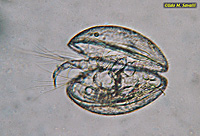
Clam shrimp (collected at Tres Rios, Tolleson, AZ) |

Vernal Clam Shrimp, Eulimnadia sp., hermaphrodite with eggs (Order Spinicaudata; native to AZ) |

Vernal Clam Shrimp, Eulimnadia sp., ventral view (Order Spinicaudata; native to AZ) |
Class Malacostraca | |||
Order Stomatopoda
|

California Mantis Shrimp, Hemisquilla californiensis |

Caribbean Rock Mantis Shrimp, Neogonodactylus wennerae, a smasher |

Mantis Shrimp, dried specimen (family Squillidae), a spearer |
Order Decapoda
| Suborder Astacidea: | ||

Burrowing Crayfish, Cambarus dubius; KY See also labeled photo. |

Northern Crayfish, Orconectes virilis, ventral view of male See also labeled photo. |

Northern Crayfish, Orconectes virilis, dissected female & male See also labeled photo. | |

Violet Reef Lobster, Enoplometopus daumi |
|
Suborder Achelata: 
California Spiny Lobster, Panulirus interruptus | |
Suborder Anomura: | |||

Orange-clawed Hermit Crab, Calcinus tibicen |

Blue-handed Hermit Crab, Pagurus samuelis, without a shell; CA |

Pacific Sand Crab, Emerita analoga | |

Pelagic Red Crab, Pleuroncodes planipes; CA |

Porcelain Anemone Crab, Neopetrolisthes maculatus, a suspension feeder |

California King Crab, Paralithodes rathbuni. | |
Suborder Brachyura (true crabs): | |||

Atlantic Ghost Crab, Ocypode quadrata; TX |

Fiddler Crab, Uca sp.; Belize |

Purple Shore Crab, Pachygrapsus crassipes; CA | |

Arrow Crab, Stenorhynchus seticornis |

Giant Spider Crab, Macrocheira kaempferi. |

Atlantic Rock Crab, Cancer irroratus; ME | |

Red Mithrax Crab, Mithraculus ruber |

Sharp-nosed Crab, Scyra acutifrons; the encrusting algae, sponges, and anemones function as camouflage |

Shield-backed Kelp Crab, Pugettia producta | |
Suborder Caridea (shrimp): | |||

Spot Prawn, Pandalus platyceros |

Tiger Pistol Shrimp, Alpheus bellulus; the nearly blind pistol shimps form mutualistic relationships with gobies: the shrimp dig the burrow and the goby is the lookout. |

Sexy Shrimp, Thor amboinensis | |

Bay Ghost Shrimp, Neotrypaea californiensis; CA |

Red Fire Shrimp, Lysmata debelius, a type of cleaner shrimp. |

Atlantic White Shrimp, Penaeus setiferus, is a commercially fished species | |

Common Fan Shrimp, Atyopsis moluccensis, a fresh-water suspension feeder. |

Cherry Shrimp, Neocaridina davidi, a fresh-water shrimp. |

Sitka Coastal Shrimp, Heptacarpus sitchensi; CA | |
Order Isopoda
|

Sowbugs, Porcellio scaber; CA |

Woodlouse, Trachelipus rathkii, ventral view; AZ |

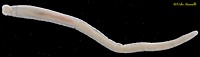
Fresh Water Isopod, Asellus sp. |

Pillbugs, Armadillium vulgare; AZ (only some isopods can roll into a ball) |

Giant Deep Sea Isopod, Bathynomus giganteus; ≈30cm long |

Intertidal Sand Isopod, Gnorimosphaeroma sp.?; CA | |

Rocky Shore Isopod, Ligia occidentalis; CA |

Scavenging Isopod, Cirolana harfodi; CA |

Large Paddle-tailed Isopod, Idotea stenops; CA | |

Spherical Isopods, Exosphaeroma inornata, an intertidal species; CA |

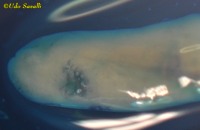
Tongue-eating Louse, Cymothoa exigua, an oral parasite of fishes; preserved specimen | ||
Order Amphipoda
|

Freshwater Scud |

Amphipod; LaJolla, CA |

Skeleton Shrimp, Caprella sp. |
(Order Mysida)
|

Opossum shrimp | ||
|
This page last updated 1 January 2025 by Udo M. Savalli () Images and text © Udo M. Savalli. All rights reserved. |