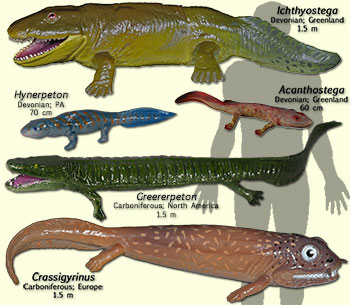
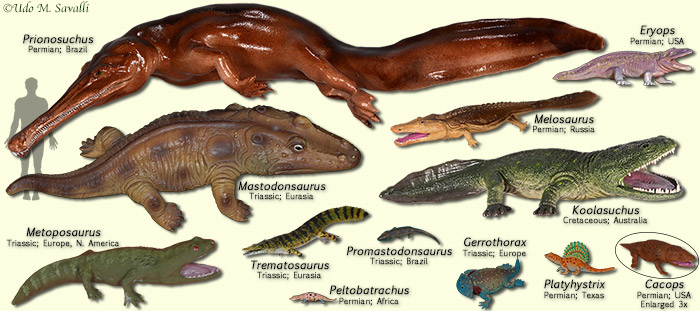
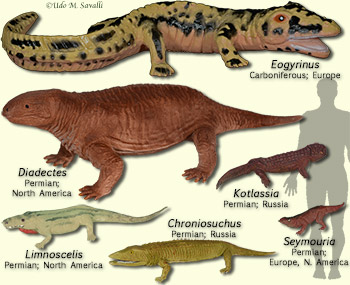
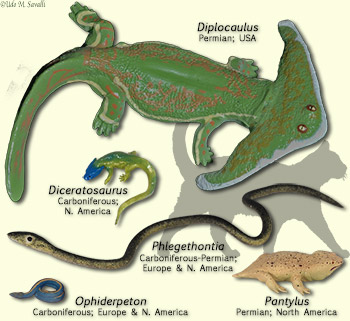
Tetrapod Characteristics
- 4 walking limbs with toes
- Specialized atlas, 2 occipital condyles
- Hyoid apparatus for tongue muscles
- Middle ear with tympanum, stapes
- Eyelids
|
Amphibia Characteristics
The following apply to Lissamphibia (extant amphibians):
- Glandular skin
- Cutaneous gas exchange
- Short ribs
- Hands with 4 digits
- Reduced or absent dermal armor
- Typically with aquatic larval stage
| |
See also Amphibian Anatomy page
|
Order Caudata — Salamanders, newts
Characteristics
- Generalized, ancestral body plan
- Elongate body, 4 walking limbs, and long tail
- Larvae differ from adults: Have tail fins, external gills, and lateral line
|

Marbled Salamander, Ambystoma opacum (Family Ambystomatidae), adult; SC; a mostly fossorial species
|

Spring Salamander, Gyrinophilus porphyriticus (Family Plethodontidae), adult; KY
|

Red-spotted Newt, Notophthalmus viridescens (Family Salamandridae); PA; terrestrial juvenile stage (larvae and breeding adults are aquatic)
|

Garden Slender Salamander, Batrachoseps major (Family Plethodontidae); CA; a fossorial, worm-like species: note reduced legs
|

Northwestern Salamander, Ambystoma gracile (Family Ambystomatidae), larva; WA
|

Spring Salamander, Gyrinophilus porphyriticus (Family Plethodontidae), larva; PA
|

Lesser Siren, Siren intermedia (Family Sirenidae), an aquatic salamander (note external gills) that lacks hind limbs
|

Chinese Giant Salamander, Andrias davidianus (Family Cryptobranchidae), the world's largest extant amphibian; aquatic
|
|
Order Anura — Frogs & Toads
Characteristics
- Body plan specialized for leaping or swimming
- Vertebral column shortened, forms urostyle
- Hind legs greatly elongated
- Fusion of tibia-fibula, ulna-radius
- Loss of tail
- Larvae ("tadpoles"): have tails, lack legs; have internal gills, have beak or denticles; lateral line present
|

Maya Mountain Frog, Rana juliani (Family Ranidae); Belize;
a semiaquatic jumper
|

Peruvian Rain Frog, Pristimantis peruvianus (Family Craugastoridae); Ecuador;
a semiarboreal? jumper
|

Sonoran Green Toad, Anaxyrus retiformis (Family Bufonidae);
a terrestrial hopper
|

Western Spadefoot, Spea hammondii (Family Pelobatidae); CA;
a burrower
|

Dyeing Dart-Poison Frog, Dendrobates tinctorius (Family Dendrobatidae); a terrestrial walker
|

Congo Spiny Reed Frog, Afrixalus osorioi (Family Hyperoliidae); Kenya; a climber
|

Veined Treefrog, Trachycephalus venulosa (Family Hylidae); Belize; a climber
|

Ornate Horned Frog, Ceratophrys ornata (Family Leptodactylidae);
a sit-and-wait predator
|

African Clawed Frog, Xenopus sp.; (Family Pipidae)
a fully aquatic swimmer
|

Tailed Frog, Ascaphus truei (Family Ascaphidae), tadpole (ventral side); CA
|

Bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana (Family Ranidae), tadpole; AZ
|

Pacific Treefrog, metamorphosing froglet, Pseudacris regilla (Family Hylidae); CA
|
|
Order Gymnophiona — Caecilians
Characteristics
- Greatly elongated, limbless bodies
- Usually have segmented rings (dermal folds)
- Eyes reduced or absent
- Most are burrowing; some aquatic
|

Gaboon Caecilian, Geotrypetes seraphini (Family Dermophiidae); a terrestrial, burrowing species from West Africa
|

Gaboon Caecilian, Geotrypetes seraphini (Family Dermophiidae); closeup of head (note lack of eyes)
|

Rubber Eel, Typhlonectes sp. (Family Typhlonectidae); preserved specimen of an aquatic species
|
|
|